IP Address stands for Internet Protocol Address. It is a logical address that is used to identify the location of a device available in a network.
There are two versions of IP Address IPv4 and IPv6.
The IPv4 is further divided into 5 classes as mentioned in the table below:
| RANGES OF IPv4 ADDRESS | ||
| Classes | Ranges | Subnet Mask |
| A | 0 – 126 | 255.0.0.0 |
| B | 128 – 191 | 255.255.0.0 |
| C | 192 – 223 | 255.255.255.0 |
| D | 224 – 239 | X |
| E | 240 – 255 | X |
Here class D and E do not have subnet mask as we do not use these two classes of address in our network. It is specially reserved for multicast and experimental or testing purpose.
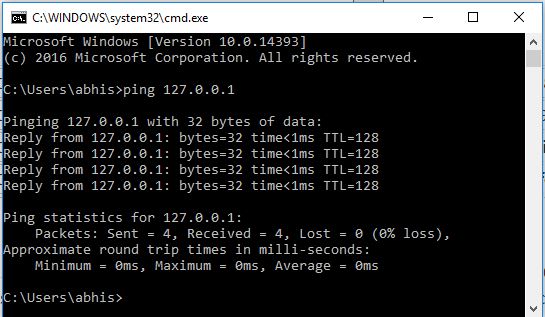
In the table,”127″ address is missing. as this range of IP addresses, we cannot use it on our networking devices. It is a loopback address. The loopback address is used to troubleshoot the network.
For example, for checking whether your NIC Card is functioning or not, go to the command prompt and ping the IP address 127.0.0.1. If you are getting a reply means your NIC Card is functioning properly.
Watch this video on IPv4 Address and its ranges
The IP Address can be static or dynamic. The static IP address is permanent and it never changes until you change it manually. The dynamic IP address is basically assigned with the help of DHCP protocol and it is not permanent. this types of address keep changes whenever your device restart.
Note:
- Ipconfig command is used to check the IP address of a system.
- Ipconfig/all command is used to check the IP Address of a system and the server.
- Ping command is used to check the network connectivity.