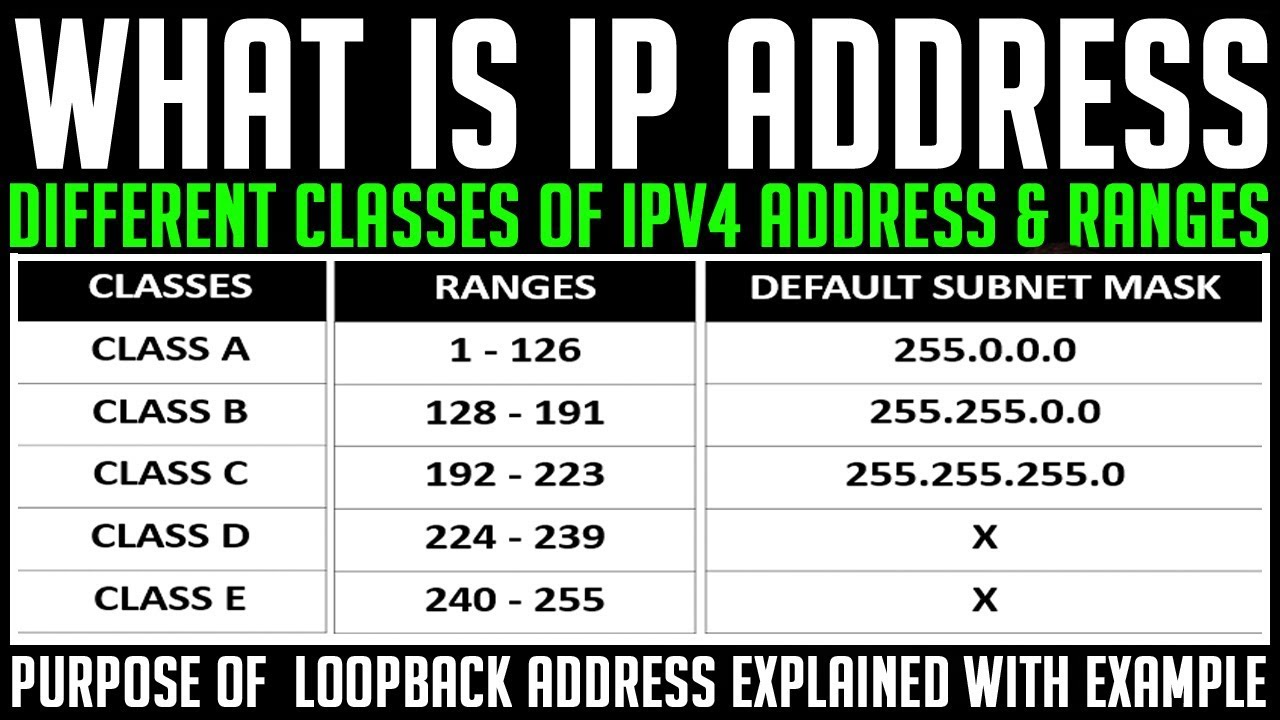
What is DNS (Domain Name System)
DNS stands for Domain Name System. It is used to translate a domain name (e.g. www.google.com) into an IP Address (192.168.10.1) or vice versa. It is very difficult to remember an IP Address of all the websites. So, we use DNS Server which helps us to convert a website name into an IP Address and allow us to access the website. Read this article till the end and you will come to know, what is DNS, how DNS works step by step, what are the functions of DNS in a computer network.
Functions of DNS (Domain Name System)
- Forward DNS Lookup and
- Reverse DNS Lookup
Forward DNS Lookup: The process of translating a domain name into an IP Address is called Forward DNS Lookup.
Reverse DNS Lookup: The process of translating an IP Address into a domain name is called Reverse DNS Lookup.
How DNS works step by step
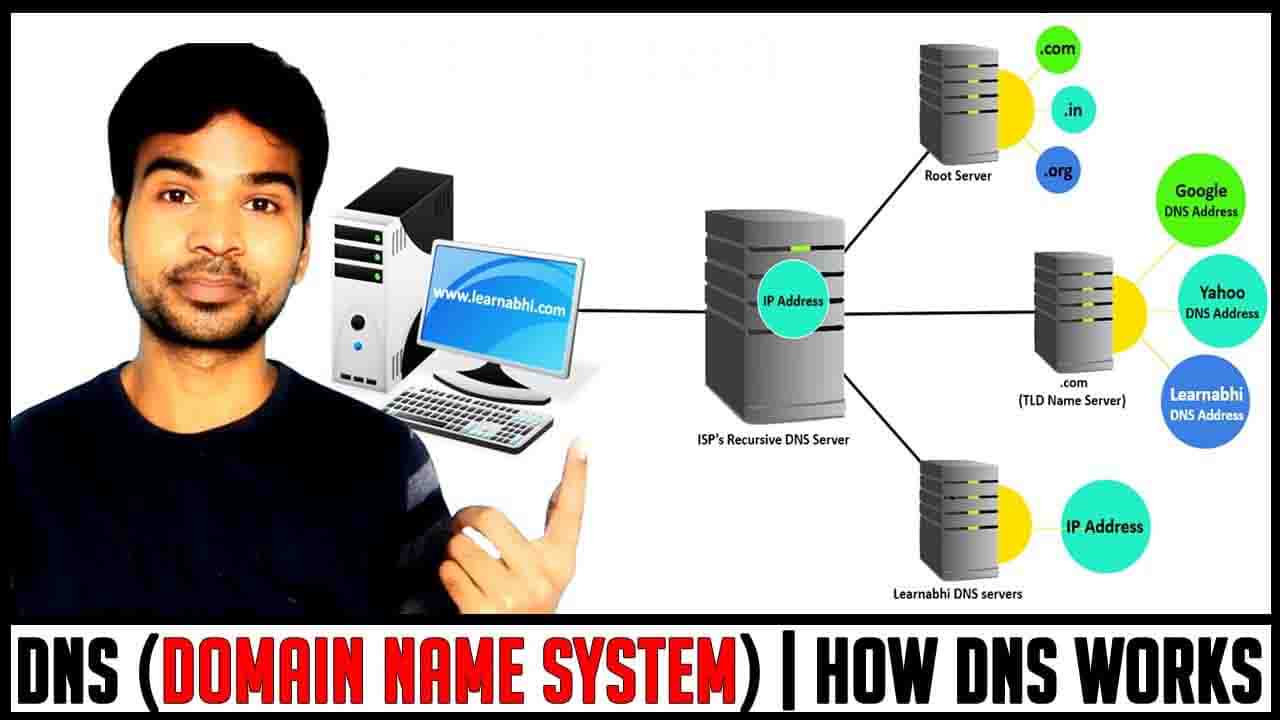
The time you enter any website name into your web browser, it cannot display the page directly because your browser doesn’t know what is the IP Address require to access the website. The first place your computer looks for the IP Address is, in its local DNS cache, which stores information that your computer has recently retrieved. If your computer doesn’t know the answer it is going to send the request to the ISP’s Recursive DNS Server.
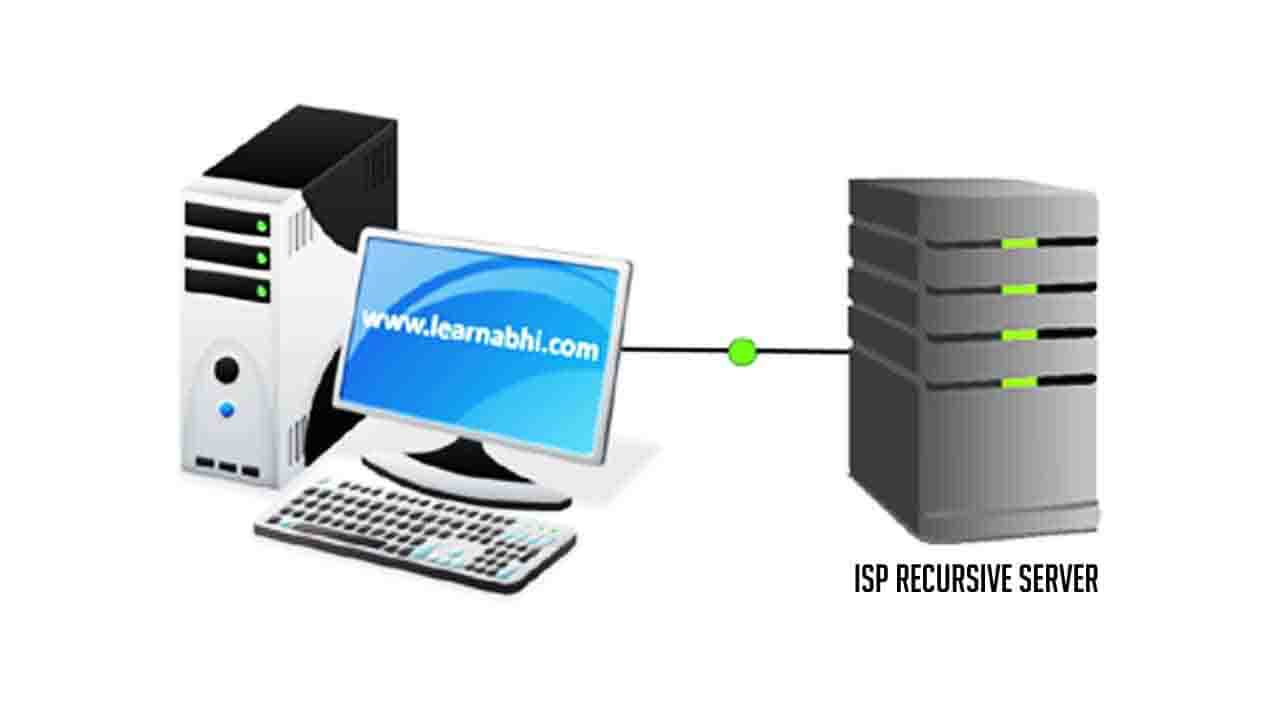
ISP’s Recursive DNS Server
Your ISP Recursive DNS Server going to check for the information in it’s Cache. If it finds the IP Address in its cache, It is going to send the information directly to your computer. If not, it is going to forward it’s requested to the Root Server.
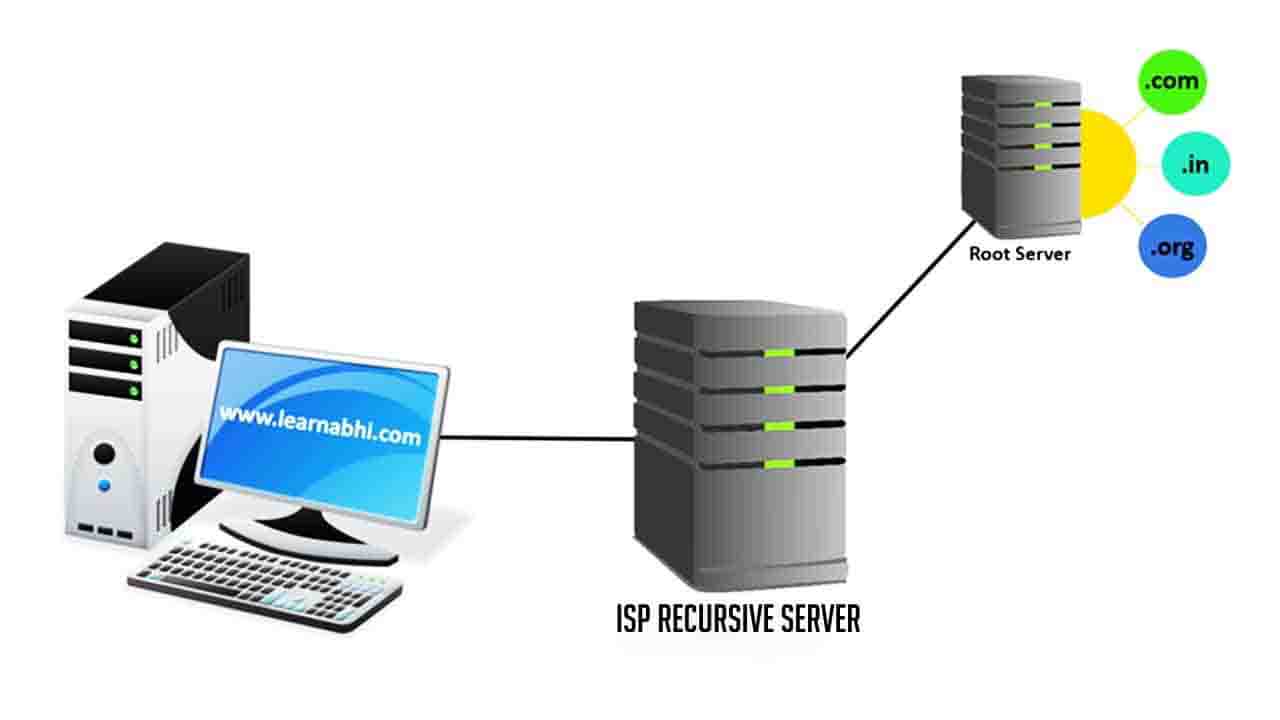
Root server
The root server act as a kind of telephone switchboard for DNS. They don’t know the answer, but they can direct our query to someone that knows where to find it. The root name servers will look at the first part of our request reading from right to left (i.e. whether our website belongs to .com, .in, .us, .org, etc.). As our website www.learnabhi.com includes .com at the first place. So, the root server will provide the address of .com TLD Name Server. Now your ISP’s Recursive DNS Server forward it’s query to the .com TLD Name Server.
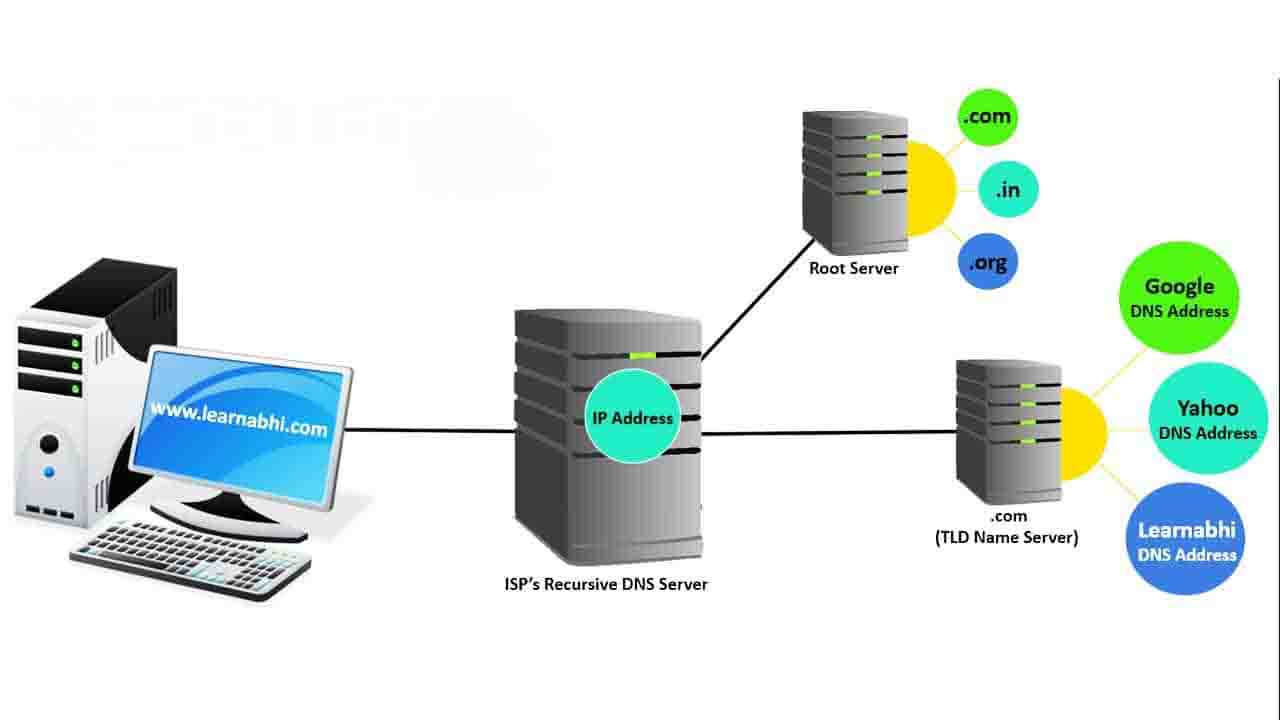
TLD NAME SERVER (.COM, .NET, .ORG, .US, IN or etc)
Each Top Level Domain (.com) stores the address information for the second-level domain (learnabhi). The TLD name servers review the next part of our request www.learnabhi.com and send the www.learnabhi.com ‘s DNS Server to the ISP Recursive DNS Server.
Now, your ISP Recursive DNS Server is going to forward its query to the DNS server of a particular domain (www.learnabhi.com) to get the IP Address.
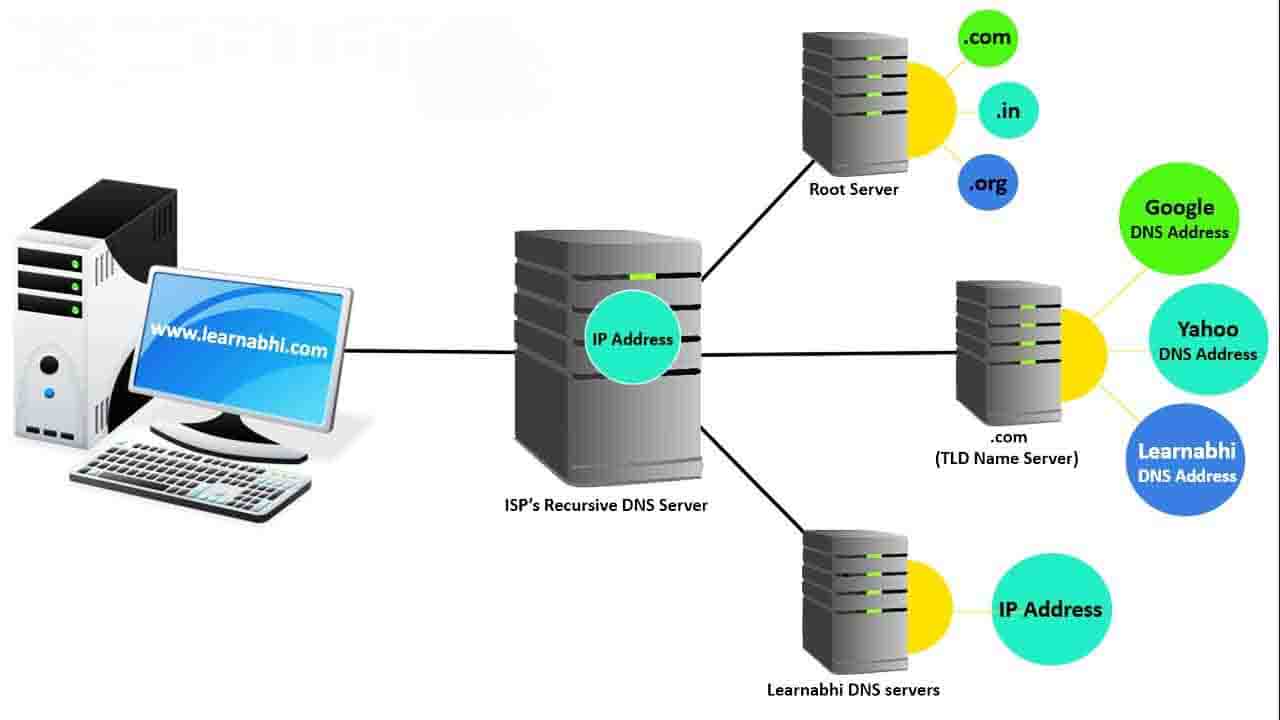
DNS Server (Domain Name Server)
These DNS servers are responsible for knowing all the information about a specific domain, which is stored in DNS records. There are many types of records, where each contains different kinds of information. In this example, we want to know the IP address for www.learnabhi.com, so it will provide the required IP Address to the ISP’s Recursive DNS Server and your ISP’s Recursive DNS Server store this address in its cache and then give the IP Address to your computer and now you are able to access the website.