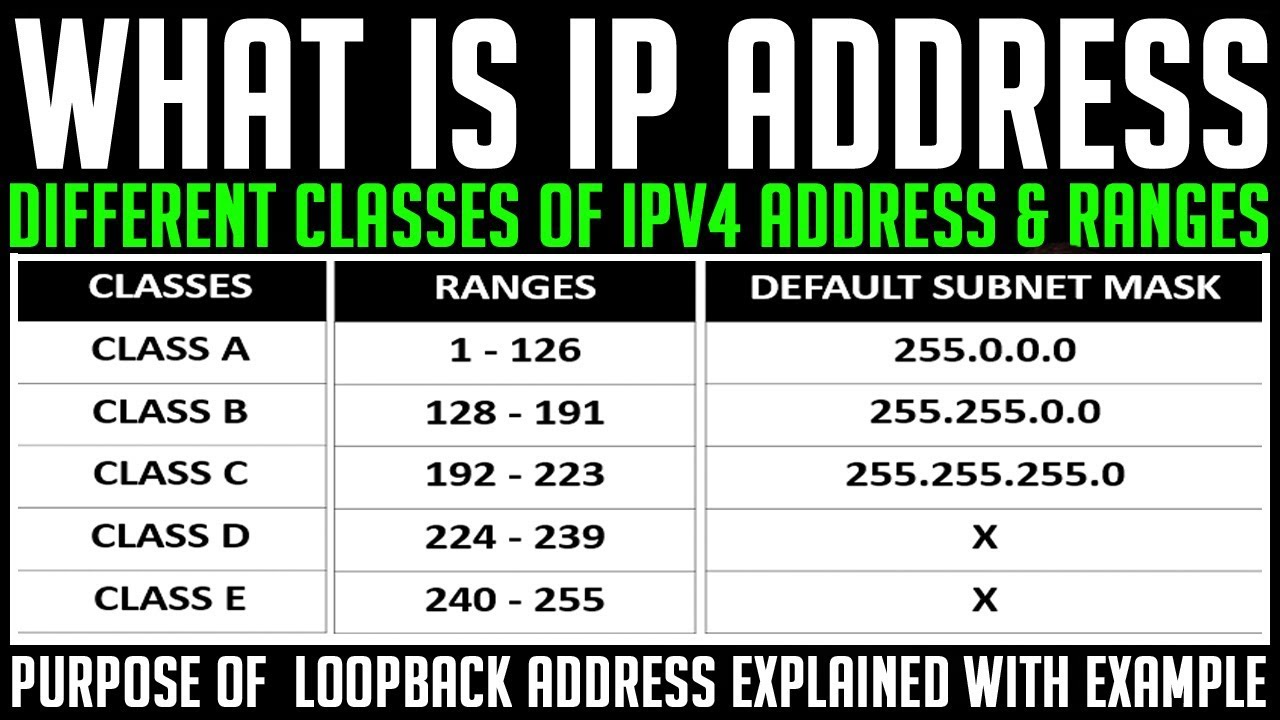
An IP Address assigned to a computer may either be a permanent address or temporary address. Hence, the address granted to a computer is divided into two categories Static IP and Dynamic IP Address and here are the differences between them.
Difference between Static IP and Dynamic IP Address
Static IP Address:
Static IP Address is assigned to the device on a network whose existence in the network remains for a longer duration such as a server. The static IP Address remains permanent into your computer until you change it manually and does not change even your computer reboot.
Advantages of Static IP Address:
- The address does not change – good for web servers, email servers, and other Internet servers.
Disadvantages of Static IP Address:
- You have to assign static IP Address manually. As for example, there are 1000 computers in an organization and you have a task to assign an IP address to each computer manually. So if you assign static IP Address to all the computer then it will be very difficult and time-consuming task for you. So, if you use dynamic IP Address then the same work can be done in a minute with the help of DHCP server.
Dynamic IP Addresses
Dynamic IP Address is assigned to the device that requires temporary connectivity to the network. The most common protocol used to assign dynamic IP Address is DHCP also called Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. The DHCP grants IP Address to a computer on lease time basis. It means, every time you restart your computer the IP address may keep the change. To find your dynamic IP address, you may visit www.whatismyip.com page.
Advantages of Dynamic IP Address:
- Cheaper than static IP address.
- Changing IP address gives more privacy.
Disadvantages of Dynamic IP Address:
- Requires DHCP server to obtain an IP address.
- Non-static. Each time IP address changes, you may have to find your IP address again.
Generally, we assign IP Address to the NIC rather than to the computer. So, if you have two NICs on your computer then you have to assign two IP Address for both NICs to communicate to the same or two different networks.