What is Hub in Networking
A Network Hub is one of the most commonly used networking devices can be easily found on any small networks such as home or office. Hub operates at the physical layer of OSI model. It is the simplest networking device hence has low cost. Basically, a hub is a repeater with multiple ports. The function of a hub in networking is similar to the repeater. It transfers data in the form of binary bits and uses for broadcasting data.
Types of Network HUB
- Passive Hub
- Active Hub
- Intelligent Hub
Passive Hub: Passive Hub does not require power as they do not regenerate the received signal before forwarding.
Active Hub: Regenerate the received signal before forwarding it to all the ports. So, the active hub needs a power supply. The small workgroup hubs normally use an external power adapter, but on larger units, the power supply is built in.
Intelligent Hub: Provides additional features to the active hub. Also known as a manageable hub, as each port on the hub can be configured by the network operator according to the network requirement. All the ports of the hub can be configured, monitored, enable or disable.
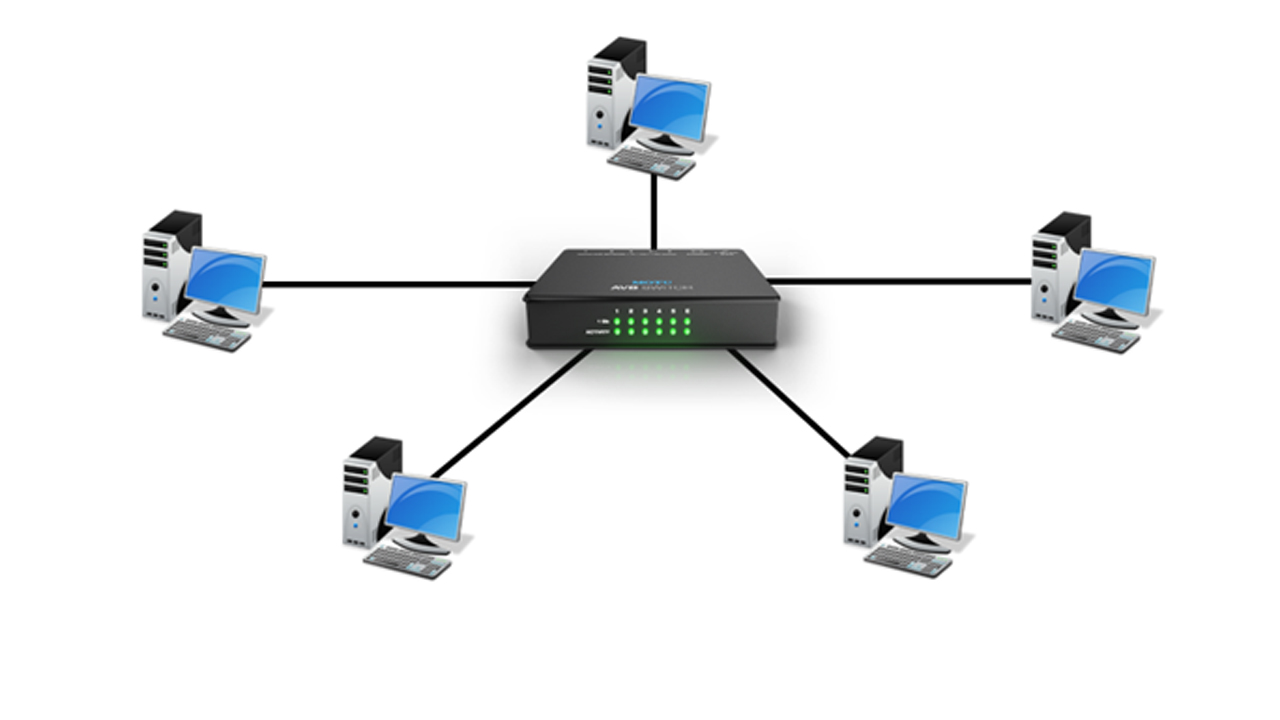
The function of a Network HUB
When a Hub receives data from one of the connected devices, it passes data to all the other ports without checking for the destination device except the port through which it receives the data. Below figure, shows the working of a HUB.
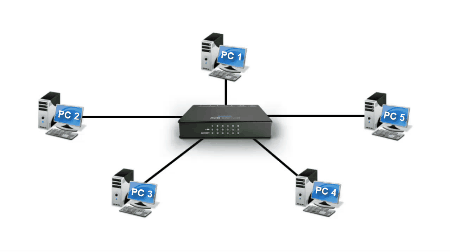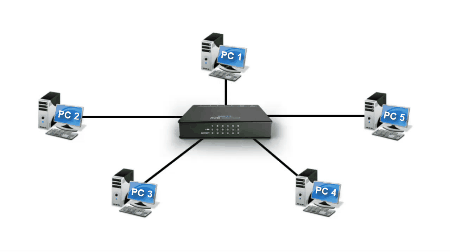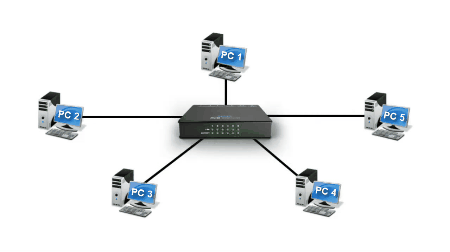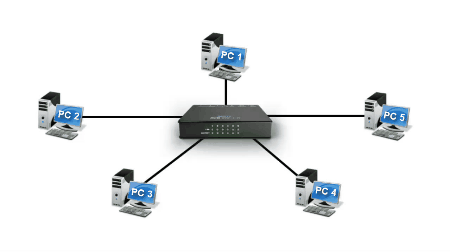
Consider, Device A want to send data to device D. When device A sends data, the hub receives it through one port and transfer the data to all the other connected devices instead of passing it to only device D. This feature of hub leads to congestion and extends the collision domain. So, it is considered as an inefficient device and needs more bandwidth for working.