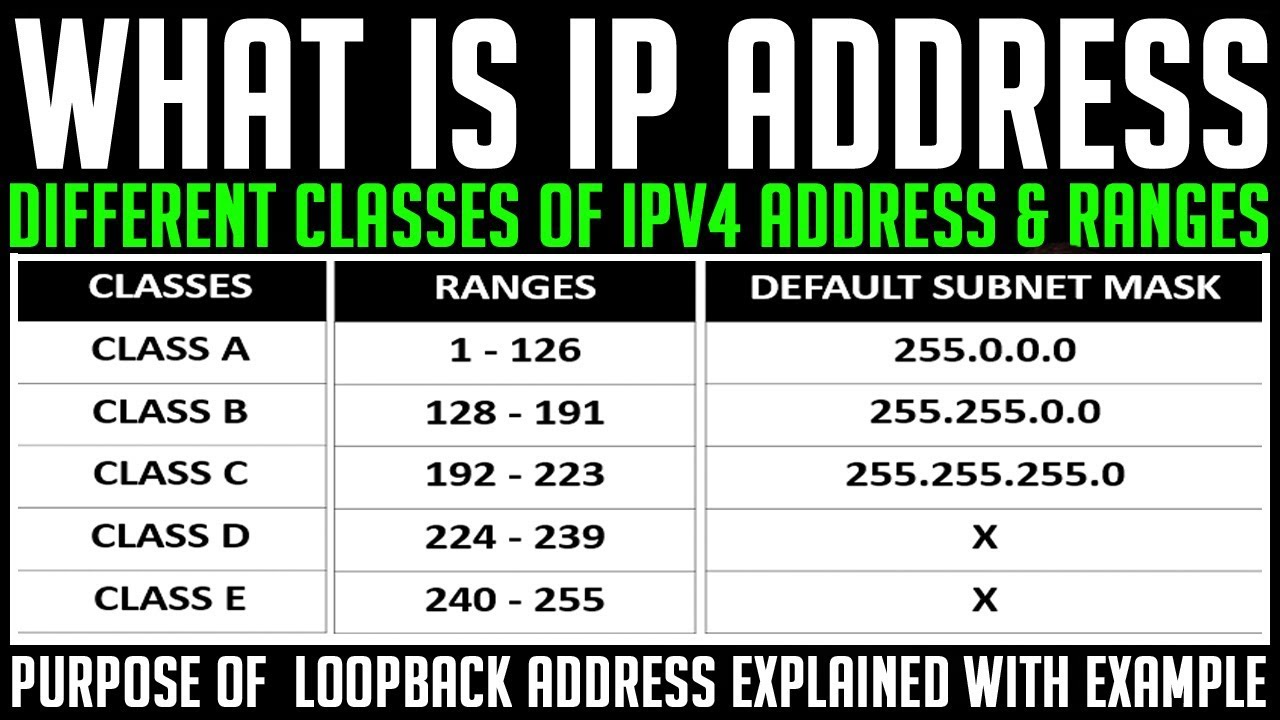
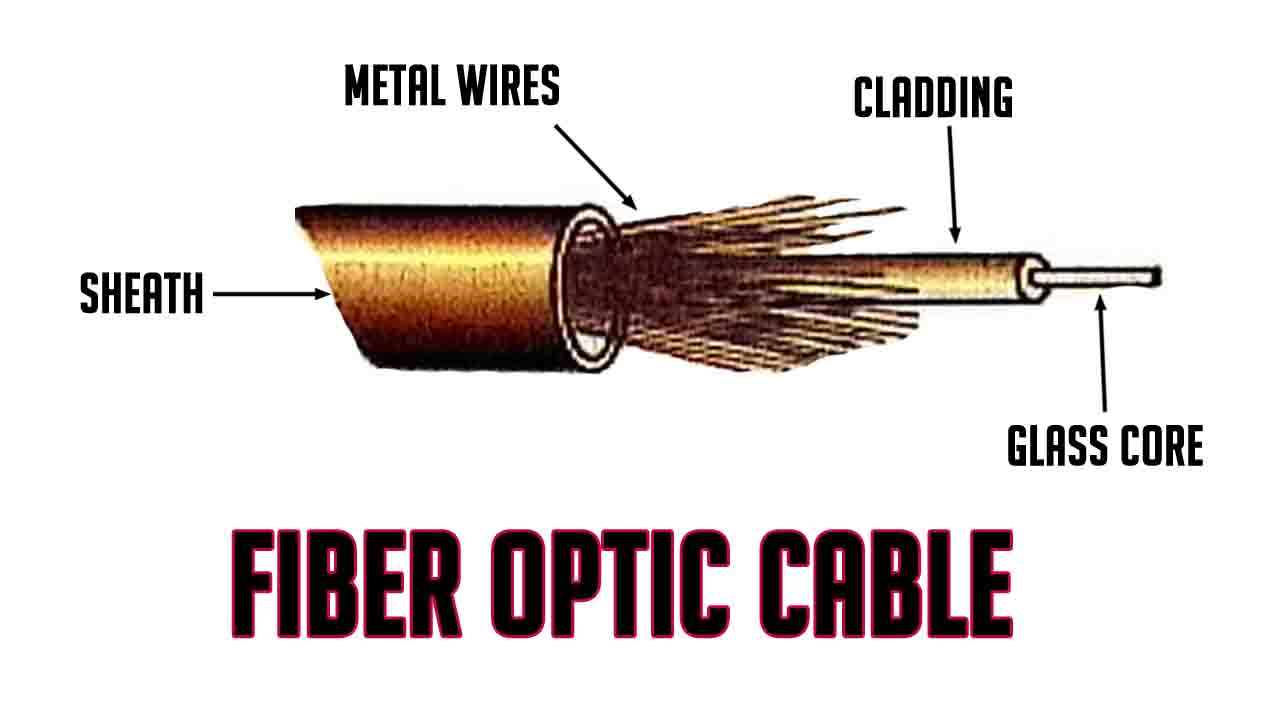
A fiber optic cable consists of a center glass core through which signals passes. It is surrounded by a glass cladding. The cladding is surrounded by PVC to increase the cable strength. This cladding is also surrounded by metal fibers to give extra strength to the cable. It Is finally surrounded by an outer cover known as a sheath as shown in the figure below.
In a fiber optic cable, the electrical signals are converted into appropriate light signals and transmitted through it. An emitter sends the signals from one end of the cable and a light sensor (Photo-detector) senses this signals and then converts into its digital equivalent. There is a transceiver located at both ends of the cable where the signals are converted from electrical to light signals and vice versa. Fiber optic cables are available in different sizes with varying core and cladding diameters. But the most commonly used fiber optic cable is the 62.5/125 micrometer. The diameter of the core is 62.5 micrometer and that of the cladding is 125 micrometer.
Characteristics of Fiber Optic Cable
| Characteristics | Description |
| Maximum cable segment length | 2 k.m. -100 k.m. |
| Bandwidth | 100 Mbps – 1 Gbps |
| Connector type | ST, SC, SMA, MIC |
| Cost | Most expensive of all types of cable |
| Interference protection | Best amongst all types of cables |
Uses of Fiber Optic Cable
Fiber optic cables are mainly used in environments that are highly susceptible to noise and other interferences. Since these cables carry light signals, they are not prone to any interference problems. These cables are highly secure as they do not emit any external signals. Fiber optic cables are used instead of copper wires due to the following characteristics:
- Bandwidth: Carries huge amount of data ranging from 100 Mbps to 1Gbps.
- Segment: length Transmits readable data signals in a range of 2 kilometers to 100 kilometers. This allows the user to transmit data over a long distance.
- Interference: Secures data from being secretly read as no electrical signals pass through these types of cables. These cables can be used in areas that are highly susceptible to noise, for example, near T.V. towers, Radio stations, Electric transformers. Copper cables are prone to interference to a certain extent.
Advantages of Fiber Optic Cable
- Able to carry much more information as compared to copper cables.
- Supports much higher data rates.
- Completely immune to crosstalk, EMI and RFI.
- Much smaller and lighter in weight as compared to copper cables.
- Unaffected by chemicals and atmospheric conditions.
- Covers large distances
- This cable is much more difficult to tap into, making it a good choice for environments with security concerns.
Disadvantages of Fiber Optic Cable
- Fiber-optic wires are difficult to install, connect and repair.
- Costly and delicate as compared to copper wires.
- More fragile than copper wires and difficult to split