UTP, STP, Coaxial and fiber optic Cable are the three most commonly used cable in a computer network. Before discussing the differences between all these cables. Let’s, understand its features, physical characteristics, advantages and disadvantages.
UTP and STP are the two types of Twisted Pair Cable. It is also known as 10BaseT where, 10 stands for 10 Mbps, the data transmission speed of cable. Base stands for the baseband signal and T stands for twisted pair cable.
UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair Cable)
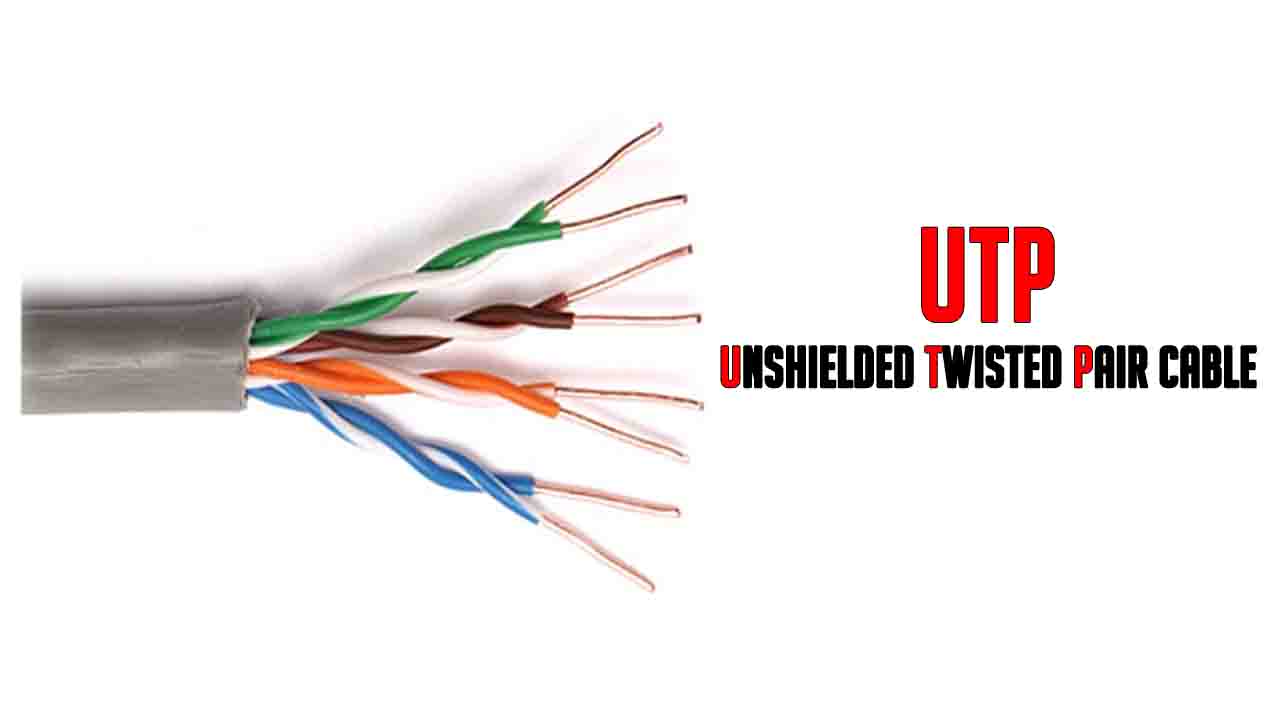
UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair Cable) is a pair of unshielded wires wound around each other. This is the cheapest form of cables available for networking purposes. It is mostly used in Local Area Network (LAN) environments. The installation cost of the cable is very cheap as it is easy to install.
Characteristics of UTP Cable
| Characteristics | Description |
| Maximum cable length | 100 meters |
| Bandwidth | 100 Mbps |
| Connector type | RJ-45 |
| Cost | Cheapest form of cable |
| Interference protection | Very poor protection from EMI and RFI |
| Bend radius | 360 degrees / feet |
| Signal transmission mode | Baseband |
| Resistance | 50 ohms |
STP (Shielded Twisted Pair Cable)

STP Cable or Shielded Twisted Pair Cable is a pair of wires wound around each other and each pair is placed inside a protective foil wrap to protect it from crosstalk. It is cheaper than fiber optic cables but more expensive than UTP. Shielded Twisted Pair Cable provides better protection from crosstalk and other interference as compared to Unshielded Twisted Pair Cable.
Characteristics of STP Cable
| Characteristics | Description |
| Maximum cable length | 100 meters |
| bandwidth | 100 Mbps |
| Connector type | RJ-45 |
| Cost | Costlier than UTP but cheaper than fiber optic cable |
| Interference protection | Better protection from crosstalk and external interference |
| Signal transmission mode | Baseband |
| Resistance | 50 ohms |
Coaxial Cable
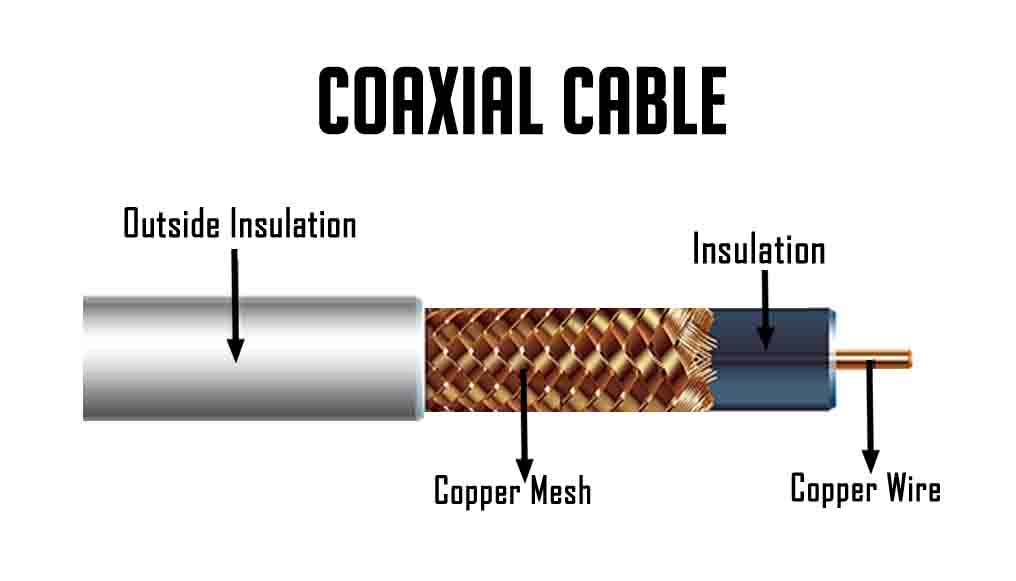
Coaxial cable is a type of copper cable specially built with a metal shield. It is primarily used by cable TV companies to connect their satellite antenna and provide facilities to the customer’s homes and businesses. Coaxial cables have concentric layers of electrical conductors and insulating material. This construction prevents the signal from crosstalk.
Fiber Optic Cable
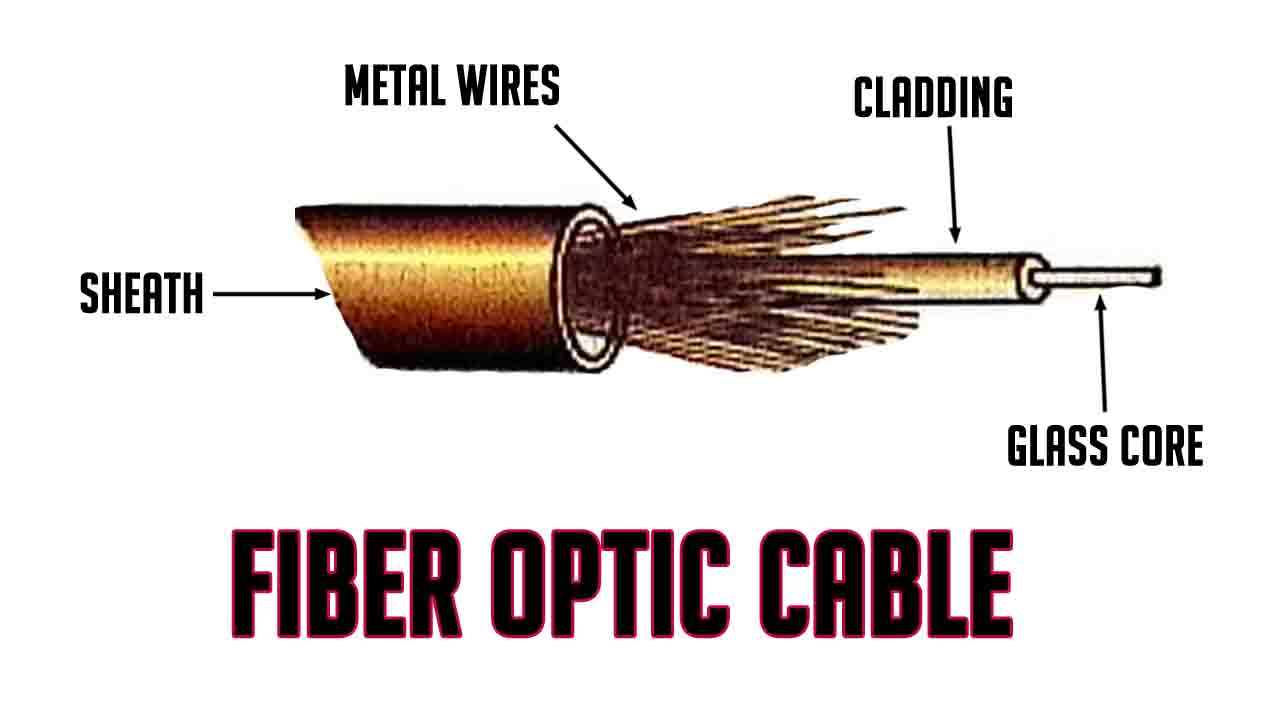
Fiber optic cables are mainly used in environments that are highly susceptible to noise and other interferences. Since these cables carry light signals, they are not prone to any interference problems. These cables are highly secure as they do not emit any external signals.
Fiber optic cables are available in different sizes with varying core and cladding diameters. But the most commonly used fiber optic cable is the 62.5/125 micrometer. The diameter of the core is 62.5 micrometer and that of the cladding is 125 micrometer.
Characteristics of Fiber Optic Cable
| Characteristics | Description |
| Maximum cable segment length | 2 k.m. -100 k.m. |
| Bandwidth | 100 Mbps – 1 Gbps |
| Connector type | ST, SC, SMA, MIC |
| Cost | Most expensive of all types of cable |
| Interference protection | Best amongst all types of cables |
Difference between UTP STP Coaxial and Fiber Optic Cable
| Characteristics | UTP | STP | Coaxial Cables | Fiber Optic Cables |
| Bandwidth | 10 Mbps – 100 Mbps | 10 Mbps – 100 Mbps | 10 Mbps | 100 Mbps -1 Gbps |
| Maximum cable segment | 100 meters | 100 meters | 200 – 500 meters | 2 k.m. – 100 k.m. |
| Interference rating | Poor | Better than UTP | Better than Twisted Pair Cable | Very good as compared to any other cable |
| Installation cost | Cheap | Costly than UTP | Costlier than twisted pair wires | Costliest to install |
| Bend radius | 360 degrees / feet | 360 degrees / feet | 360 degrees / feet or 30 degrees / feet | 30 degrees / feet |
| Security | Low | Low | Low | High |