A computer network can be wired and wireless. A network can be categorized as per the geographical area to be covered by the network. The computer network includes LAN (Local Area Network), CAN (Campus Area Network) MAN (Metropolitan Area Network), and WAN (Wide Area Network). Before discussing the difference between LAN CAN MAN and WAN in tabular form. Let’s understand the basic concept of these network types.
There are four types of Network
- LAN
- CAN
- MAN
- WAN
LAN (Local Area Network)
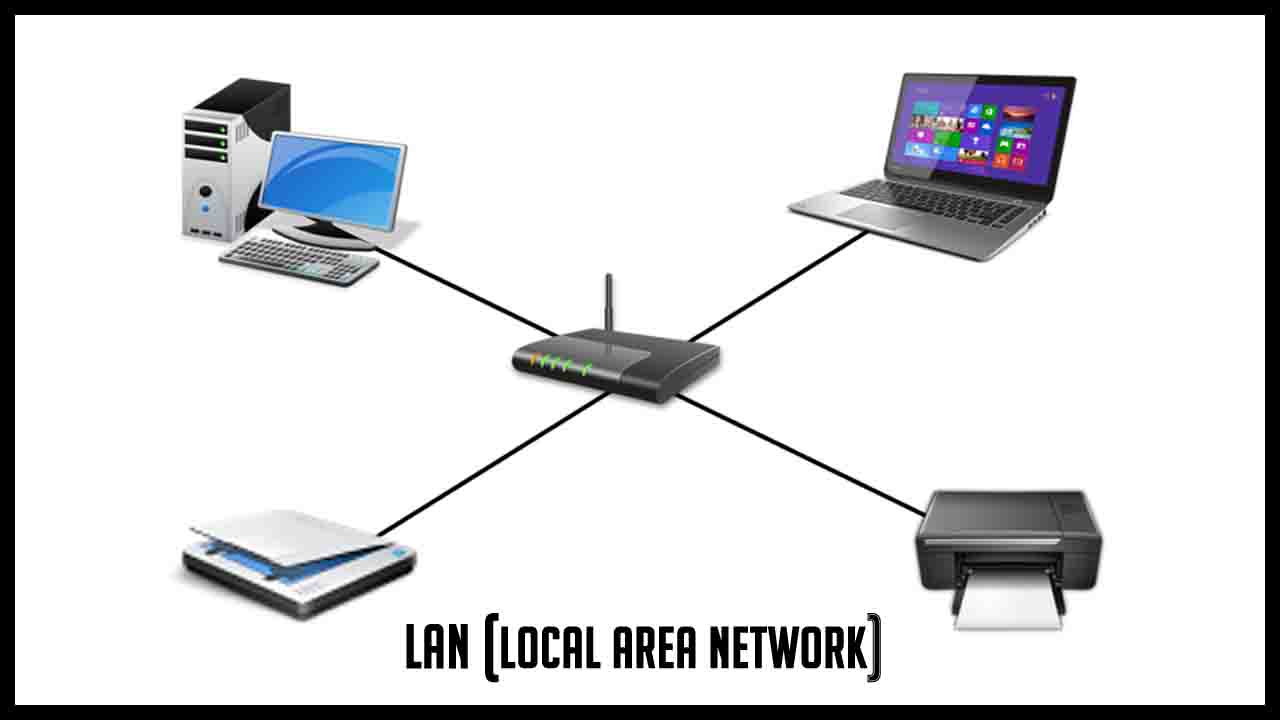
LAN is a computer network that spans over a small area. It connects computers and workstations to share data and resources such as printers or faxes. LAN is restricted to a small area such as home, office, or college. However, one LAN can be connected to other LANs over any distance via a telephone line and radio waves.
CAN (Campus Area Network)
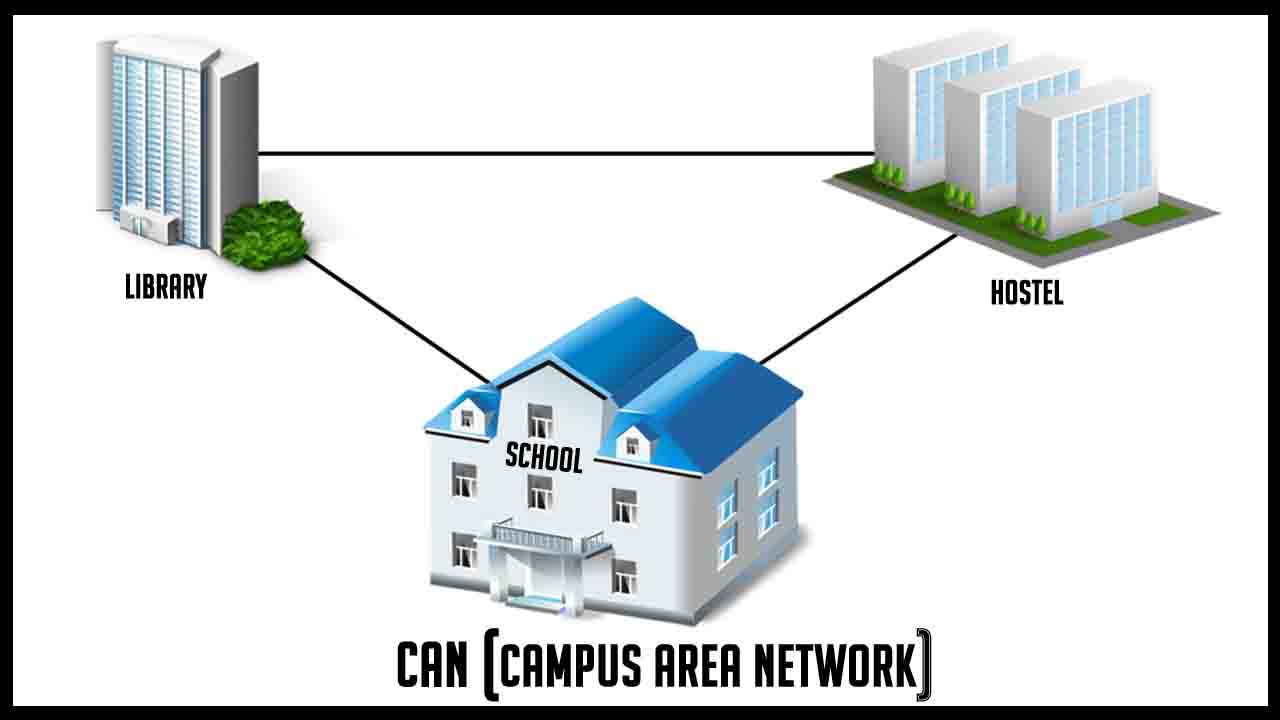
It is a computer network made up of two or more LANs within a limited area. It can cover many buildings in an area. For example, different buildings on campus can be connected using CAN. It will help to interconnect academic departments, library and computer laboratories. CAN is larger than a LAN but smaller than WAN.
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
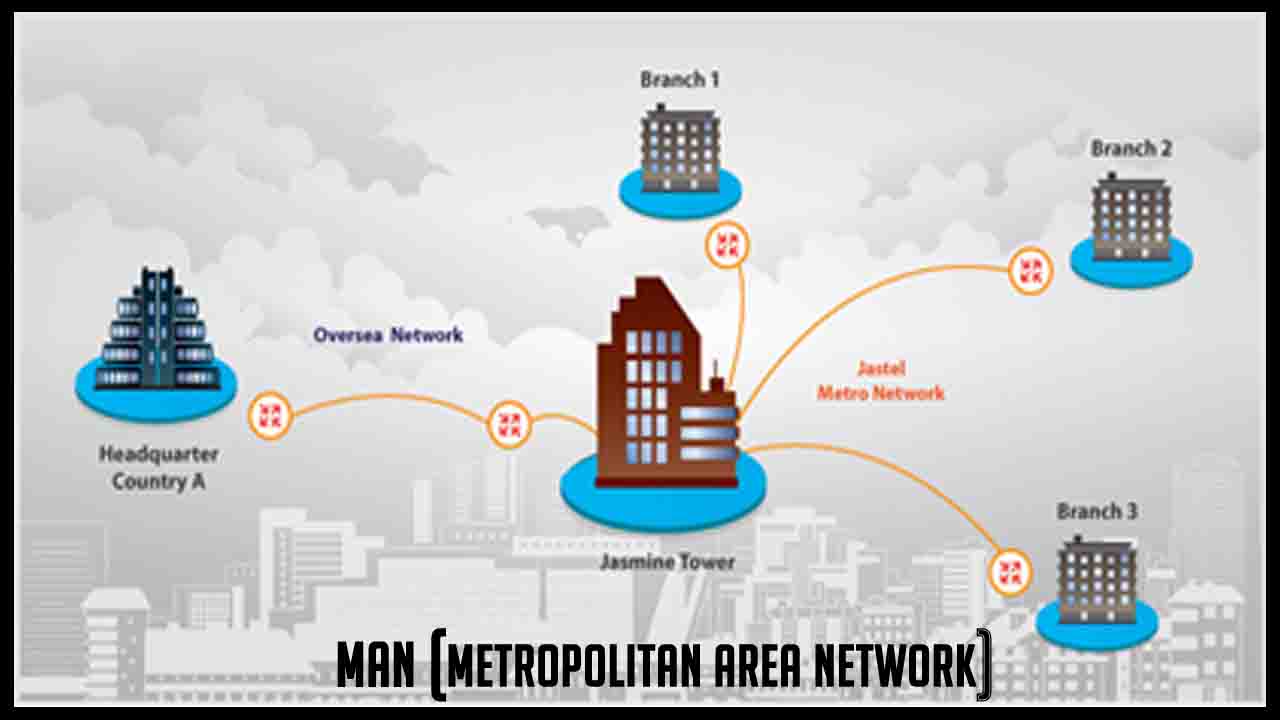
MAN is the interconnection of networks in a city. It acts as a high-speed network to allow sharing resources within a city. MAN supports data and voice transmission both. The best example for MAN is the television cable network in cities. MAN is larger than LAN and CAN but smaller than WAN.
WAN (Wide Area Network)
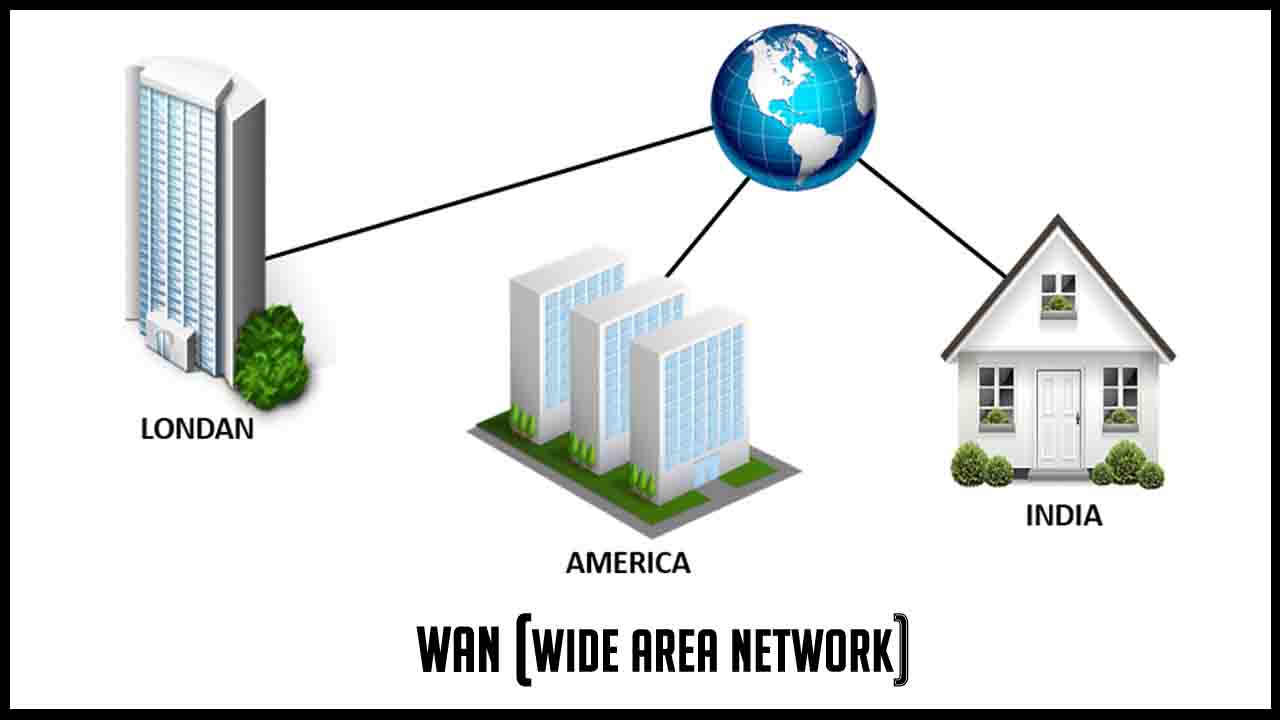
It covers a wide geographical area that includes multiple computers or LANs. WAN connects computers through public networks, like telephone systems, microwaves, satellite links, or leased lines. Most of the WANs use leased lines for Internet access as they provide faster data transfer.
WAN helps an organization to establish a network between all its departments and offices located in the same or different cities. It also enables the communication between the organization and the rest of the world.
Difference between LAN CAN MAN and WAN in Tabular Form
LAN |
CAN |
MAN |
WAN |
| LAN stands for Local Area Network | CAN stands for Campus Area Network | MAN stands for Metropolitan Area Network | WAN stands for Wide Area Network |
| Connects computers and workstations in the office or home. | Connects two or more LANs within a campus | Interconnects network in a town or a city. | Connects geographically separated LANs. |
| Covers a local area of 1 KM. | It covers a privately-owned campus with an area of 5 to 10 KM. | It covers larger areas than LAN but a small area than WAN with an area or 2 to 100 KM. | Spans large geographical area more than 100 KM. |
| Data transmission rate 10/100/1000 Mbps. | The data transmission rate is variable. | The data transmission rate is variable. | The data transmission rate is from 64Kbps to 150 Mbps. |
| Cheaper | Expensive then LAN | Expensive than LAN and CAN | Most Expensive |
| Uses the IEEE 802 standard. | – | Uses the IEEE 802 standard. | Uses the ITU standard. |
| Networking devices such as repeater, hub, and switch are used in LAN | The networking devices such as a hub, switch, Bridge, and gateway are used. | Networking devices such as a hub, switch, gateway, router, and brouter are used. | Networking devices such as a hub, switch, gateway, and router are used. |
| Less Congestion | More congestion compare LAN | More congestion compare LAN and MAN | Most congestion netwok compared to LAN, CAN, and MAN. |
Difference between LAN CAN MAN and WAN short video